Introduction
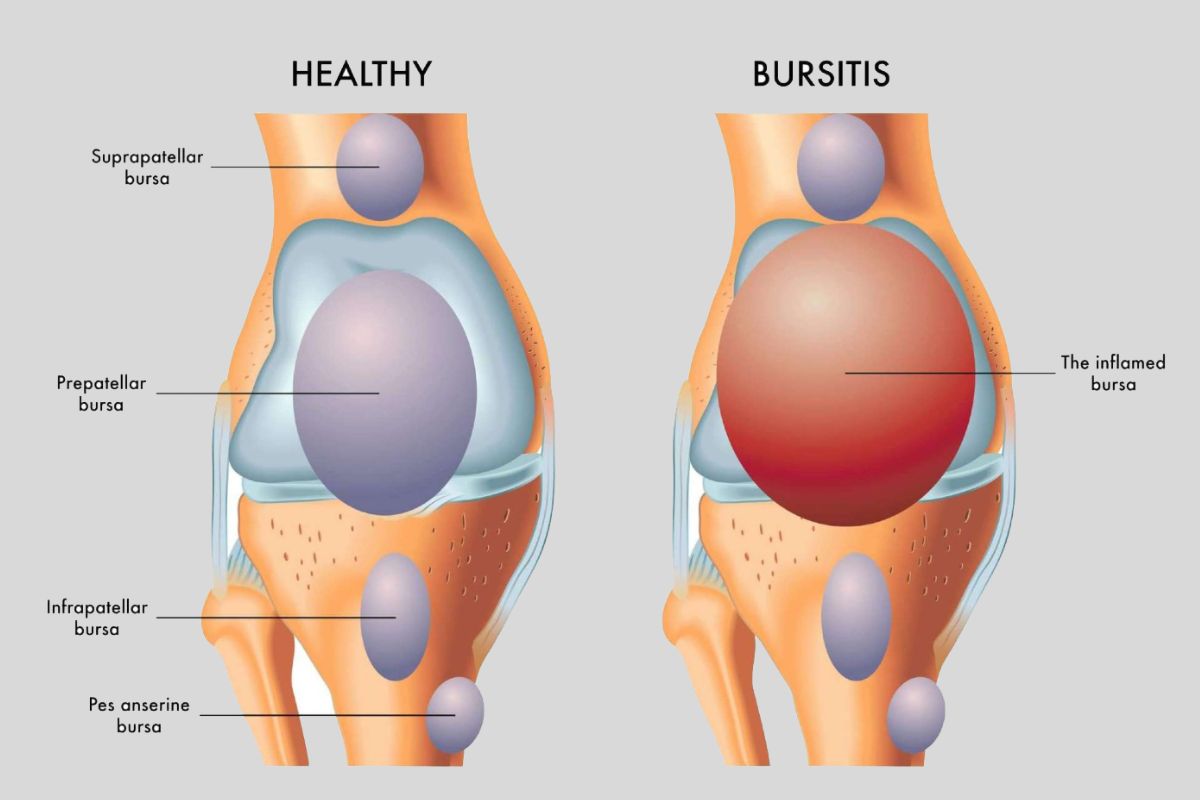
What is Bursitis?
Causes of Bursitis
- Repetitive Motion: Activities involving repetitive movements or prolonged pressure on a joint, such as throwing a baseball or kneeling, can lead to bursitis.
- Injury: Sudden trauma to a joint can cause the bursa to become inflamed.
- Infection: Although less common, bursitis can result from an infection in the bursa.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes increase the risk of developing bursitis.
- Age: Bursae may become more susceptible to inflammation as we age.
Symptoms of Bursitis
- Pain that worsens with movement or pressure
- Swelling and redness around the joint
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Warmth in the affected area
Treatment Options
1. Physical Therapy
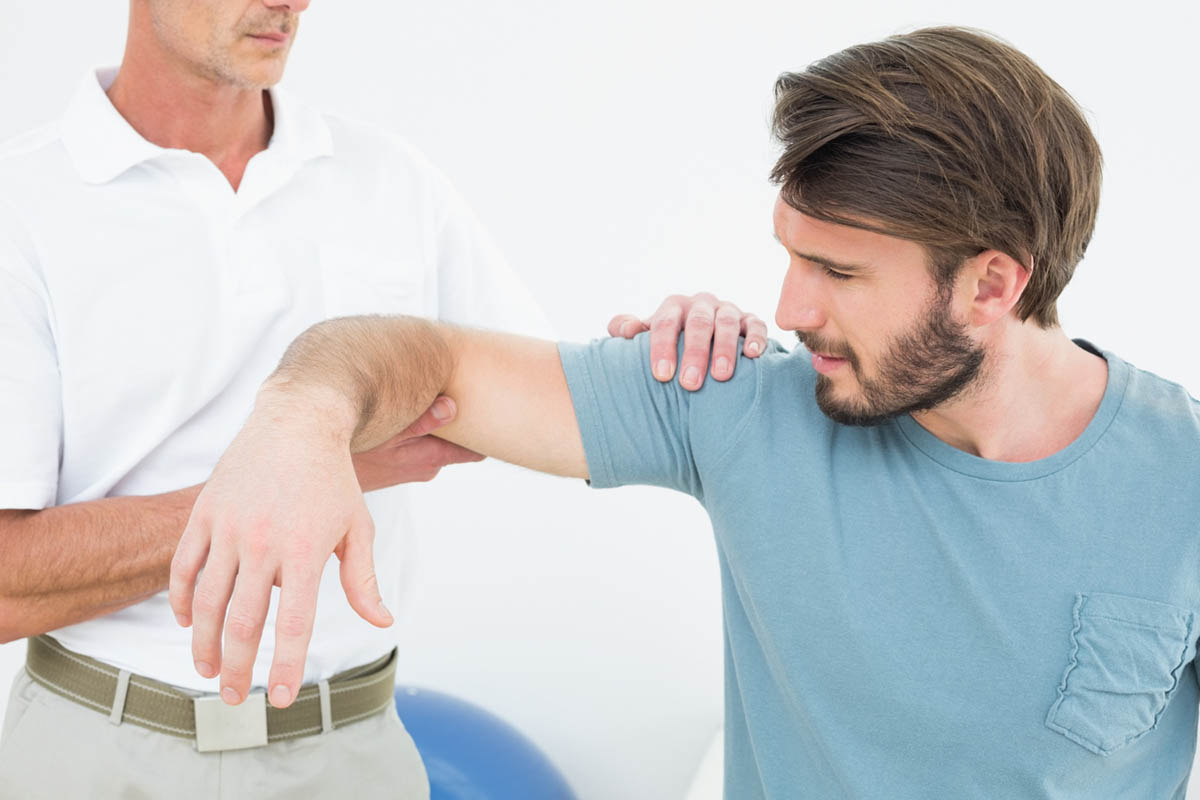

Physical therapy is crucial for managing bursitis and preventing future flare-ups. A physical therapist can develop a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improve flexibility, and reduce stress on the bursa. At Revival Physical Therapy in Minneapolis, we offer customized treatment plans designed to help you recover quickly and effectively.
2. Rest and Activity Modification
Avoid activities that aggravate the condition and give the affected joint time to heal. Gradually reintroduce activities as pain and swelling decrease.
3. Ice Therapy
Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain. Use an ice pack for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
4. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce severe inflammation.
5. Compression and Elevation
Using compression wraps and elevating the affected joint can help reduce swelling.
6. Aspiration
In cases where the bursa is significantly swollen, a doctor may perform a procedure to remove excess fluid from the bursa.
Preventing Bursitis
- Warm Up Properly: Always warm up before physical activity with gentle stretching and light aerobic exercises to prepare your muscles and joints.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle support around your joints and reduce the risk of bursitis.
- Flexibility Exercises: Regularly stretch your muscles and joints to maintain flexibility and reduce tension.
- Use Proper Techniques: When performing activities with repetitive movements, use proper techniques to prevent overuse injuries.
- Take Breaks: If your work or hobbies involve repetitive movements, take regular breaks to rest and stretch your joints.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Keeping a healthy weight can reduce stress on your joints and lower the risk of bursitis.
Real-Life Case Study: Lisa’s Recovery from Shoulder Bursitis
FAQs
Q: How long does it take to recover from bursitis?
A: Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the condition and how well you adhere to the treatment plan. Most people recover within a few weeks with proper care and rest.
Q: Can bursitis become a chronic condition?
A: If left untreated or if the underlying causes aren’t addressed, bursitis can become a chronic condition. It’s important to follow a comprehensive treatment plan to prevent recurring episodes.
Q: Are there any exercises I should avoid if I have bursitis?
A: Avoid exercises that put excessive pressure on the affected joint or involve repetitive movements that can aggravate the condition. A physical therapist can provide guidance on safe exercises and modifications.
Q: Can I treat bursitis at home?
A: Mild cases of bursitis can often be managed at home with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment guidance.